Secrets of Chiral Gas Chromatography (Chiral GC): How to Understand
Table of Contents
- Introduction and outcome
- Chiral Stationary Phases in Chiral GC
- Principle and Chiral separation mechanism
- Selection of Chiral stationary phase/column
- Advancements in Chiral GC
- Can Achiral compounds can be separated along with Chiral isomers?
- Limitations of Chiral gas chromatography
Introduction and Outcome: Chiral Gas Chromatography (Chiral GC)
Chiral Gas Chromatography (Chiral GC) is widely used to determine the optical purity of volatile pharmaceuticals at every stage during drug development. It gives fast, specific, precise, accurate and reliable results. Secondly, the Chiral GC analysis cost is lower than the Chiral HPLC technique. However, chiral GC method development is a challenging task for any chromatographer. That is why I decided to share my expertise on this topic. In this article, I will discuss the GC chiral stationary phases, the selection of the chiral stationary phases and their advantages. After reading this article, you will understand the Secrets of Chiral Gas Chromatography.
What is the Need for Chiral Gas Chromatography?
More than 80% of active pharmaceuticals are chiral. The compounds in the human body are also chiral. Therefore the human body often responds differently to enantiomers, one form may produce the desired effect while the other may be ineffective or toxic. Therefore, it is crucial to separate enantiomers in the pharmaceuticals to ensure the desired therapeutic outcomes. Several chromatographic techniques are used for chiral separation and one of them is Chiral gas chromatography.
What is the Chiral Gas Chromatography (Chiral GC)
The process of separation volatile pharmaceuticals using GC with a capillary column containing a chiral stationary phase is is called Chiral Gas Chromatography (Chiral GC)
Chiral GC Columns or Chiral GC Stationary Phases
The following chiral stationary phases (CSPs) are widely used in Chiral GC :
- Cyclodextrin derivative
- Amino acid derivatives, and
- Metal coordination complexes.
Among the above CSPs, cyclodextrin-based stationary phases are the most widely used and popular.
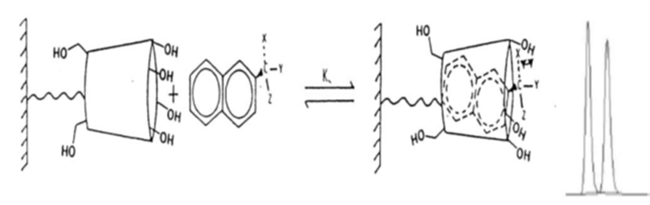
Principle and Chiral separation mechanism
Separation is achieved by Incursion complexing and Hydrogen bonding
How to Select Chiral stationary phase/column?
Selection of the CSPs depends upon the polarity and nature of the molecules (e.g. volatile nature of pharmaceuticals)
- Use amino CSPs for amino compounds
- Use cyclodextrins CSP for hydroxyl Chiral compounds
Can Achiral impurities be separated along with Chiral isomers?
The answer is yes and it is two-dimensional GC technique .
The two-dimensional GC technique is a powerful tool for the separation of achiral isomers as well as enantiomers of Chiral pharmaceuticals. For this, two columns are connected in the series using a union. The first column is an achiral column and the second column is a chiral column.This heart-cutting technique allows for the selective separation of the target enantiomeric compounds as well as achiral impurities. In a single run, one can get both the achiral impurities profile and chiral purity of the Enantiomeric molecules.
Advancements Chiral stationary phases (CSPs)
In addition to cyclodextrin derivatives, other types of chiral stationary phases such as cyclofructans, metal-organic frameworks, porous organic cages, and chiral ionic liquids are also used in chiral GC. These phases also offer unique selectivity and have specific applications in the separation of different types of enantiomeric compounds.
Case Studies: How to develop chiral purity method of Menthone?
Following is the structure of menthone:
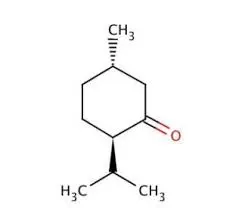
Menthone has two chiral centres and hence it will have four chiral isomers. All four chiral isomers can be separated by chiral gas chromatography using Beta Cyclodextrin CSPs.
Advantages of Chiral gas chromatography
Chiral GC offers several advantages, including high efficiency, sensitivity, and fast analysis. That is why this is the widely used technique in pharmaceutical development. The following are the advantages of the Chiral GC:
- Fast analysis
- Low analysis cost
- Reproducible result
- Better resolution between the isomers (R)
- High column efficiency (N)
- Sharp and symmetrical peaks
- Acceptable by Regulatory agencies
- Easy to validate the method
- Suitable for volatile molecules
- High sensitivity or low detection limit
- The separation of complex samples containing multiple enantiomeric pairs can be achieved through two-dimensional GC (2D-GC) techniques.
- Chiral GC with a mass detector (GC-MS) can be used for identification and structure elucidation of unknown isomers during pharmaceutical development
Limitations of Chiral gas chromatography
Not suitable for non volatile Chiral molecules like steroids, amino acids, Carbohydrates’, Antibiotics…
Conclusion
Chiral gas chromatography is a powerful technique for the separation of Enantiomers of various volatile pharmaceuticals. Hope this post has cleared all your doubts related to Chiral gas chromatography and you can replicate the same during Analytical method development for chiral molecules. Write your opinion or questions related to this article in the comment sections.
You may also want to check out other articles on my blog, such as:
- Difference between HPLC and GC
- How to develop a method using GC-MS?
- Need of Chromatographic Method in Drug Development
- How to develop GC method?
- How to decide system suitability test (SST)?
- Allowable GC Method Adjustment
- What should be the Analytical method development approach?
FAQs
What is chiral gas chromatography?
The separation of volatile chiral pharmaceuticals/molecules using chiral capillary stationary phases (CSPs) is called chiral gas chromatography.
What is the principle of chiral chromatography?
The separation of chiral compounds in chiral GC occurs due to the interaction of different isomers between the CSPS and the carrier gas. Separation is achieved by inclusion complexing and hydrogen bonding.
What is the mechanism of chiral chromatography?
In chiral chromatography, separation is achieved by the inclusion complexing and hydrogen bonding while using cyclodextrin CSPs
Can chiral separation be achieved using GC?
This can be achieved by GC using chiral capillary column
What are the limitations of Chiral gas chromatography?
Not suitable for non volatile Chiral molecules like steroids, amino acids, Carbohydrates and Antibiotics.
Abbreviations:
- GC: Gas chromatography
- CSPs: Chiral stationary phases
References:
- USP
- Analytical chemistry Gary D christian
- https://pharmaknowledgeforum.com/why-is-chiral-separation-so-important/
- Practical high-performance liquid chromatography: Veronica R. Meyer
- Separation of Enantiomers with ChiraDex®



 Previous Post
Previous Post
Excellent article sir …if possible please include derivatisation methodology also sir..
Noted. Derivatization methodology will be included soon.