Potency, Purity and Assay
Table of Contents
Introduction and Background
Potency, purity and assay are highly used terms in pharmaceutical analysis and they play an important role in pharmaceutical analysis. Be it qualitative analysis (such as identification by HPLC, GC, UV, FTIR, GC-MS and LC-MS) or quantitative analysis (such as assay and content testing), standards are used everywhere. However, chemists have a lot of confusion related to the use of these terms. That is why I decided to share my skill-based knowledge on these terms. In this article, I will discuss potency, purity and assay, the difference between potency, purity and assay, calculation of potency, purity and assay, case studies and frequently asked questions.
Related Post: How To Calculate Potency, Purity and Assay In Pharmaceuticals: Accurate and Easy Approach
Potency, Purity and Assay
Purity
Purity is the qualitative content of any drug substance or its stages. It may be calculated by chemicals, spectroscopic and chromatographic techniques. Chemicals and spectroscopic methods of calculating the purity are not specific and selective and that is the reason these methods are rarely used for calculating the purity. But chromatographic methods are specific and selective and that is the reason chromatographic methods are used for calculating the purity in Pharmaceutical industries.
Chromatographic methods for calculating the Purity
Purity can be calculated using chromatographic techniques like high-pressure liquid chromatography HPLC), Gas chromatograph (GC) etc as per method requirements. The following methods are used in the industries for calculating the purity:
- Area normalisation method and
- External standard method
Area normalisation method or area% method
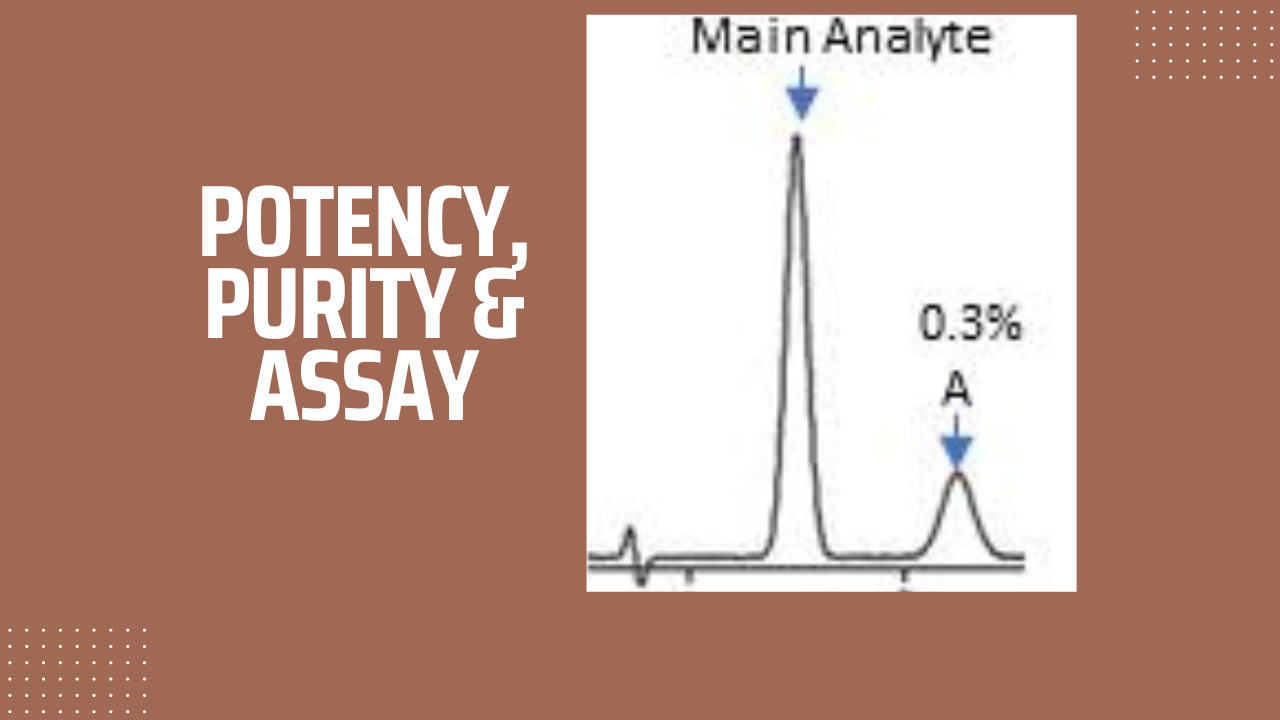
Impurities peaks (having value ≥ Quantitation limit or QL) as well as main analyte peak are integrated and purity is calculated using the following formula:
% Purity = (Area response of Main analyte /Sum of area response of all peaks)X100
External standard method
In this method each impurity is calculated against either diluted standard of main analyte or against their corresponding impurity (as per method). Purity is calculated using following formulae:
Purity= (100 – sum of all impurities* present in the chromatogram)
Note*:
- Only those impurities having value ≥ Quantitation limit or QL are considered in purity calculation
- Purity is applicable for both standard and samples
Potency
Potency is the exact quantitative content of a drug substance or its stages. It is only applicable to standards. The highest pure material is used to calculate the potency. All types of impurities like organic impurities, inorganic impurities, residual solvents, counter ions, loss on drying or water content are taken into consideration for potency calculation.
Procedure for calculating the potency
First purity is calculated as per prescribed method of analysis. Then after potency is calculated using following formulae:
Potency = Purity – (Sulphated ash/residue of ignition + Loss on drying/water content/residual solvent + counter ion) etc..)
Assay
The Assay is the quantitative content of a drug substance or main analyte. It is a relative value and it is calculated against its corresponding standard while using chromatographic technique or spectroscopic technique. The potency of the standard is required in the assay calculation while using the chromatographic technique or spectroscopic technique.
The Assay can also be calculated using the chemical titration technique and in this technique, there is no need of any external standard. Since the chemical technique is not specific and that is why it is rarely used in the pharmaceutical industries.
Procedure for calculating the Assay
Generally, the following formulas (1- External standard method and 2- internal standard method) are used for assay calculation:

Case study: Potency, Purity and Assay
If a drug substance has an impurity A is 0.3%, LOD is 1.0%, and sulphated ash is 0.1%. calculate purity and potency
- Purity = 100 – 0.3 = 99.7%
- Potency = Purity – (LOD + sulphated ash) = 99.7 – (1 + 0.1) = 98.6%
Difference between Purity, Potency and Assay
| Purity | Potency | Assay |
| It is qualitative content of a drug substance or a molecule | It is quantitative value of standard | It is quantitative value of a drug substance or a molecule |
| It is absolute value | It is absolute value | It is relative value |
| Purity depends upon related organic impurities | Potency depends upon purity LOD/water, ROI or sulphated ash, in-organic impurities, counter ions, residual solvents etc. | Assay depends upon potency ( while using spectroscopic and chromatographic techniques). |
Also Read: Analytical Method Development and Validation
Applications
- Purity is applicable for both standard and sample and purity is used to calculate the potency of the standard.
- Potency is related to only standard and it is used to calculate assay. It is the absolute value.
- The assay is the relative value and it is calculated using the potency of the standard
Conclusion
Purity, potency and Assay are related to each other and widely used terms in pharmaceutical industries. I hope all your doubts related to purity, potency and assay would have been cleared. For any query related to this article write in the comment section and I will answer on a priority basis.
To deepen your understanding of Potency, Purity and Assay be sure to check out this article:
How To Calculate Potency, Purity and Assay In Pharmaceuticals
FAQs (Interview questions on potency, purity and assay)
What does purity and potency mean?
Both purity and potency tell about the exactness of the pharmaceutical. Purity is the qualitative value whereas potency is the quantitative value. Secondly, potency is only applicable for standard whereas purity is applicable for both standard and sample.
How to calculate potency from an assay?
Potency is not calculated from assay, but the assay is calculated from potency. Potency is calculated from purity.
Abbreviations
- ROI: Residue on ignition
- LOD: Loss on drying
- GC: Gas chromatography
- HPLC: High pressure liquid chromatography
- MS: Mass spectroscopy
- UV: Ultra violet spectroscopy
- FTIR: Fourier transform interferometer
References:
- USP
- IP


