Difference Between HPLC and GC: How to Understand Easily
Table of contents
- Introduction and Background
- HPLC & GC
- Applications of HPLC
- Applications of GC
- Difference between HPLC and GC
- Case studies
- Conclusion
Introduction and Background
High-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) and Gas chromatography are widely used instruments in Pharmaceutical industries. Now the question is what is the difference between HPLC and GC? Most of the chemists have a lot of confusion related to their use which is why I decided to share my skill-based knowledge on this topic. This article will clear all your doubts related to the difference between HPLC and GC and you can easily select the suitable instrument during the method development. H
HPLC & GC
HPLC
High-pressure liquid chromatography is a separation technique based on solid stationary phase and liquid mobile phase and separations are achieved by partition, adsorption or ion exchange processes depending upon the type of stationary phase used. The following are the different components of HPLC:
- Mobile phase
- Degasser
- Pump
- Mixing valve
- Guard column
- Sample injection port
- Injector
- Column
- Column temperature controller
- Detector waste collector
- Data processor &
- Chromatogram
Applications of HPLC
HPLC is used for both quantitative and qualitative analysis in industries like:
- Pharmaceuticals
- Testing laboratory
- Research centres
- Biotech industries
- Pesticide industries
GC
GC (Gas chromatography) is a chromatographic technique for the separation of volatile components. In GC components to be separated are distributed between two phases, one of them is stationary phase and the other is mobile phase is gas which moves percolating through the stationary phase. The chromatographic process occurs as a result of repeated sorption-desorption acts during the movement of the sample components along the stationary phase and the separation is due to differences in the distribution coefficient of the sample components. The following are the different components of GC:
- Carrier gas ( Generally Helium and Nitrogen are used)
- Flow control valve
- Sample injection port
- GC column (Now a days only capillary columns are used)
- Column oven temperature controller
- Detector
- Outlet
- Data processor &
- Chromatogram
Applications of GC
GC is used for qualitative and quantitative analysis of volatile molecules in several industries:
- Pharmaceuticals
- Air pollution
- Foods
- Pesticides residues
- Petroleum industries
- Essential oils
- Testing laboratory
Differences between HPLC and GC
| S.N | HPLC | GC |
| 1 | It is used for both non volatile and volatile molecules | It is used only for volatile molecules |
| 2 | Most widely used detector is UV. Other detectors like ELSD, RI, ECD, Mass, Corona/CAD, FD..are also used | The most widely used detector is FID. Other detectors like TCD, ECD, NP, Mass..are also used |
| 3 | Compound must have UV absorption | Compounds must have oxidisable carbon atoms |
| 4 | Volatile components with UV absorption can be analyzed on HPLC using UV detector e.g. Benzene, Toluene… | Non volatile components with oxidisable carbon atom can not be analysed on GC with FID detector e.g. Carbohydrates, antibiotics… |
Case studies
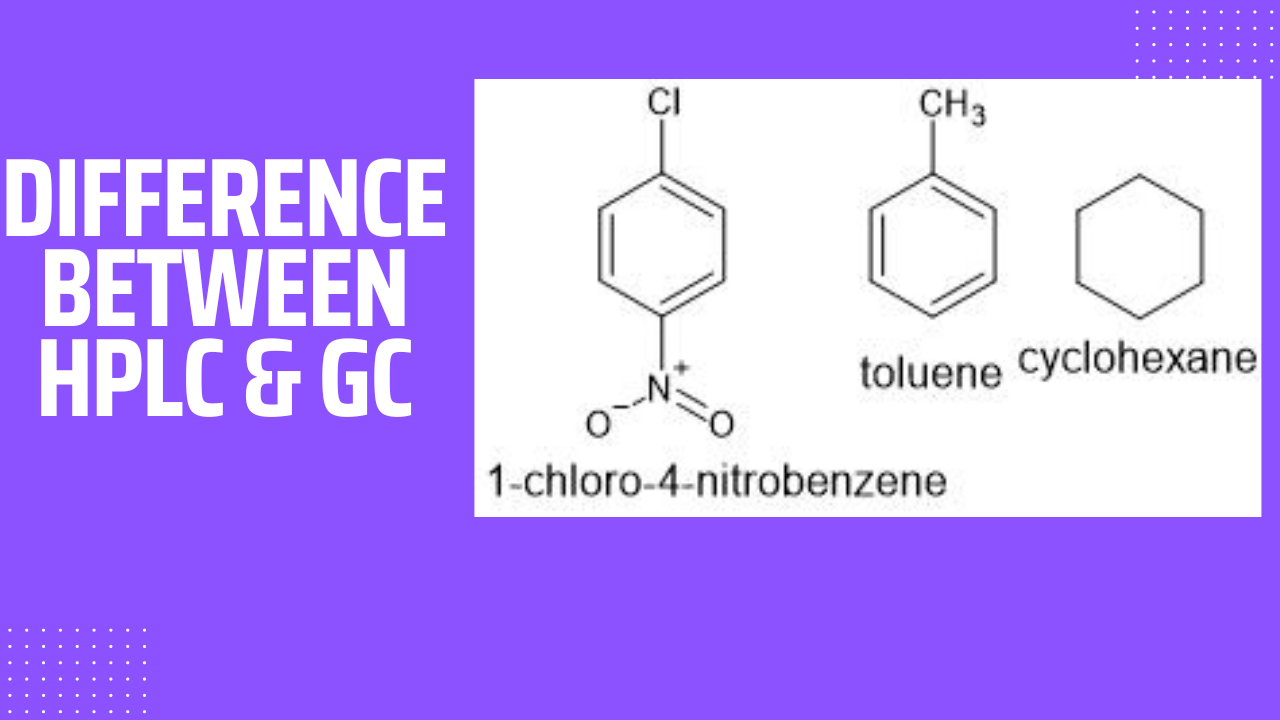
Analysis of para chloro nitro benzene, Toluene and cyclohexane

1-chloro-4-nitrobenzene
It has very good UV absorption and hence it can be analysed by HPLC. Due to high V.P, it can not be analysed by GC
Toluene
It has UV absorption and it is a volatile molecule with oxidisable carbon atoms. Hence it can be analysed on GC using an FID detector as well as HPLC using a UV detector.
Cyclohexane
It has no UV absorption and hence it can not analysed on HPLC using a UV detector. It is a volatile molecule with an oxidisable carbon atom and hence it can be analysed on GC using an FID detector.
Conclusion
Both HPLC and GC play vital roles in pharmaceutical development. I hope that this post has cleared up all your doubts about the selection of HPLC and GC. If you have any questions related to this blog, write in the comment section, and I will answer them as soon as possible. You may also want to check out the following articles:
- How to develop method by GC?
- How to adjust system suitability parameters in GC?
- Top GC interview questions and their answer
- How to develop an analytical method by HPLC?
- How to adjust HPLC method?
- How to develop method on LC-MS?
- How to develop method on GC-MS?
FAQs
What is HPLC?
What is GC?
For which type of molecules GC should be used?
For which type of molecules HPLC should be used?
What is the differance between HPLC and GC?
What are the limitations of GC and HPLC?
What are the different components of HPLC?
What are the different components of GC?
Can HPLC be used in place of GC?
Can GC be used in place of HPLC?
What are two advantages of HPLC over GC?
What is the difference between liquid liquid chromatography and gas liquid chromatography?
What is the difference between GPC and HPLC?
References
- IP
- USP
Abbreviations
- FID: Flame ionisation detector
- GC: Gas chromatography
- HPLC: High – pressure liquid chromatography
- ELSD: Evaporation light scattering detector
- FD: Flurorance detector
- ECD: Electrochemical detector
- ECD: Electron capture detector
- BP: Boiling point



Very good information.
Very good information.
Also write something on column chemistry
Excellent representation of difference of two widely used analytical methods in chromatography
Well done 👌
Perfect summary for beginners
Perfect summary for beginners…
Excellent representation of difference of two widely used analytical methods in chromatography
Well done 👌
Plz sir topic for method development for HPLC