HPLC Column: How to Select
Introduction and outcome
HPLC column is responsible for the separation of various analytes from the sample mixture. No matter how sophisticated HPLC system is, separation will not occur if the column is not in good /running condition. That is why I decided to share skill-based knowledge on this topic. In this article, I will discuss HPLC column chemistry, its types, applications, management, advantages, factors affecting stability of the HPLC column and frequently asked questions.
Table of content
- Introduction and outcome
- HPLC column
- 4 types of HPLC columns
- HPLC column chemistry and analyte suitability
- HPLC column selection procedure
- HPLC column performance controlling parameters
- Factors affecting HPLC column stability
- Characteristics of a good column
- Applications
- Commonly used HPLC column#in
- Conclusion
- FAQs
HPLC column
HPLC column is made of stainless steel, polymer (such as polyetheretherketone) or combination of stainless steel and polymer. It is filled with the stationary phase and stationary phase is responsible for separation of the analytes from the sample mixture. It is denoted like
C18, (250×4.6)mm, 5µm
Where: C18 represents the octadecyl phase of the column, 250 mm represents length of the column, 4.6mm represents diameter of the column and 5µm represents the particle size of the column
4 types of HPLC columns
- Reverse phase chromatography (RPC) column: In RPC column nonpolar stationary phase is used and in this column first polar analyte elutes and then non polar analyte elutes. In case of Benzoic acid and Toluene, first Benzoic acid and then after toluene will elute;. Typical RPC columns are C18, C8 and C4
- Normal phase chromatography (NPC) column: In RPC column polar stationary phase is used and in this column first nonpolar analyte elutes and then polar analyte elutes. In case of Benzoic acid and Toluene, first Toluene will elute and then after Benzoic acid will elute;. Typical NPC columns are Silica, diol and alumina.
- Size exclusion chromatography (SEC) column
- Ion exchange chromatography (IEC) column
HPLC column chemistry and analyte suitability
The Siloxane (-Si-O-Si-) type of bonded phase is widely used for the commercial purpose. It is formed by di or tri alxoy silane with surface silanol groups of fully hydroxylated silica gel
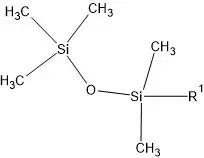
R1 decides the type of column in the RPC mode.
| R1 | HPLC column | Column selection and analyte suitability |
| -CH3 | C1 | It is used in reverse phase chromatographic (RPC) mode for isomeric separation |
| -CH2-CH3 | C2 | It is used in reverse phase chromatographic (RPC) mode for isomeric separation of hydrophobic molecules. Retention time is longer than the C1 column |
| -CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3 | C4 | It is used in reverse phase chromatographic (RPC) and ion-pair reverse phase mode (IPRPC) for macromolecules. Retention time is longer than the C2 column |
| -(CH2)7-CH3 | C8 | It is used in reverse phase chromatographic (RPC ) and ion-pair reverse-phase ((IPRPC)) mode for moderately polar compounds such as steroids and nucleoids. Retention time is longer than the C4 column |
| -(CH2)17-CH3 | C18 | It is used in reverse phase chromatographic (RPC) mode and ion-pair reverse-phase (IPRPC) mode for separation of moderately polar and non-polar compounds such as amino acids, poly steroids and glycerides. Retention time is longer than the C8 column |
| -(CH2)3CN | Cyno | This is the universal column and it is used in both reverse phase chromatographic (RPC) mode and normal phase chromatography (NPC) mode. In reverse phase chromatographic mode it is used for separation of macromolecules. |
| -(CH2)3-Ph | Phenyl | It is used in reverse-phase chromatographic (RPC) mode and ion-pair reverse-phase mode for separation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, polar aromatic compounds, fatty acids and separation of isomeric compounds |
| -(CH2)3-NH2 | Amino | It is used in normal-phase chromatographic (NPC) mode for separation of substituted aniline, esters, chlorinated pesticides and carbohydrates |
Polymer columns
Polymer column is packed with polystyrene divinylbenzene. This column is used in reverse phase chromatographic mode for the separation of macromolecules such as Erythromycin and Azithromycin.
Silica columns
The stationary phase in silica column is Silica gel. This column is used for separation of polar compounds in normal phase chromatographic mode.
HPLC column selection procedure
The following components are considered during column selection during the method development
- Length of the column: On increasing the column length separation between peaks is increased.
- Particle size of the stationary phase: On decreasing the stationary phase particle size peak sharpness and separation between the adjacent peak is increased. Hence HPLC column with smaller smaller stationary phase should be preferable choice,
- Stationary phase purity: Stability of a column depends upon the purity of the stationary phase. Hence HPLC column with pure stationary phase should be preferable choice,
- Carbon load: HPLC column with high carbon load should be preferable choice,
- Column temperature: Generally on increasing the column temperature peak sharpness as well as separation between adjacent peak is increased
HPLC column performance controlling parameters
System suitability test (SST) is used to to check the performance of a HPLC column. SST may contain two or more than two of the following chromatographic terms:
- Column efficiency or theoretical plate (N)
- Tailing factor (T)
- Resolution (R)
- Capacity factor (K)
- Void volume
- Peak shape: Sharper the peak better is the column
Factors affecting HPLC column stability
The following components affect the stability of the HPLC column:
- Temperature: As the temperature increases stability of the stationary phase decreases. Try to perform analysis at around ambient temperature
- pH: The Siloxane (-Si-O-Si-) bonded phase is stable between pH 2 to 8. Hence try to keep mobile phase pH between 3 to 6
- Flow rate: Higher flow rate decreases the stability of the HPLC column
- Buffer concentration: On increasing buffer concentration stability of stationary phase decreases. Hence try to keep buffer concentration as low as possible in the mobile phase
- Column washing and storage: Clean and wash the column as per procedure.
Characteristics of a good column
The following are the characteristics of the good column:
- High carbon loading
- High end capping
- High sensitivity
- Wide application range
- Small particle size
- Shorter analysis time
- Base to base separation between the adjacent peaks
Applications
HPLC columns are used in both qualitative analysis (like identification test, purity test, monitoring the reaction) in the following industries:
- Research and development centre
- Pharmaceutical industries
- Food industries
- Beverage industries
- Testing laboratory
- Pesticide industries and
- Polymer industries
Commonly used HPLC column
C18 and C8 columns are highly used columns in reverse phase chromatography mode. Cyano column is the universal column and it is used in both reverse phase mode and normal phase mode.
Conclusion
HPLC column play a crucial role in separation of the various components in the sample mixture. HPLC column selection needs both knowledge and skills. Now I hope, this post has cleared all you doubts related to HPLC columns and increased your knowledge to the next level. For any question or more information related to HPLC column selection you can contact me using contact form.
You may also want to check out other articles on my blog, such as:
- Difference between HPLC and GC
- How to develop a method using LC-MS?
- Need of Chromatographic Method in Drug Development
- How to decide system suitability test (SST)?
- Allowable HPLC Method Adjustment
- How to develop the HPLC method for basic compounds?
- How to develop the HPLC method for acidic compounds?
- How to develop the HPLC method for non-polar compounds?
- What should be the Analytical method development approach?
FAQs
What is the HPLC column procedure?
HPLC column is made of stainless steel or polymer and filled with stationary phase. It is responsible for separation of analytes from the sample mixture
What are the factors affecting life of a HPLC column?
Factors like temperature, pH, buffer concentration and pressure affects the life of the HPLC column.
What are the performance parameters of the HPLC column?
HPLC column performance is decided by column efficiency, tailing factor, HETP and resolution
What is the pore size in the HPLC column?
The pore size determines whether an analyte can diffuse in and out of the stationary phase packing.The pore size is the average size of the pores in porous packing of the stationary phase. Its unit is angstrom(A)
What is the most commonly used column?
C18 and C8 are the most commonly used column .
Why is C18 column mostly used in HPLC?
C18 contains octadecyl hydrocarbon. Octadecyl hydrocarbon is a chain 18-carbon atom (nonpolar chain) and makes the column stable across a wide range of pH. That is why C18 column mostly used in HPLC.
What are the most common HPLC columns?
In reverse-phase chromatography, the most commonly used columns are C18, C8 and Cyno. In normal phase chromatography, the most commonly used column is Silica
What is the full name of C18?
Octadecyl
Is C18 polar or nonpolar?
Nonpolar
What C4 C8 and C18 columns are meant for?
C4 contains butyl hydrocarbon chain, C8 contains octyl hydrocarbon chain and c18 contains octadecyl hydrocarbon chain
Why is silica polar in HPLC columns?
The surface of silica is covered with silanols (Si-OH). This -OH is a polar functional group. This -OH group make silica column polar.
What are the different types of HPLC columns?
Different types of HPLC columns are reverse phase chromatography column, normal phase chromatography column, size exclusion chromatography column and ion exchange chromatography column
Abbreviations
- HPLC: High performance liquid chromatography
- RPC: Reverse phase chromatography
- NPC: Normal phase chromatography
References
- Practical high performance liquid chromatography;Veronica R. Meyer
- Analytical chemistry; Gary D. Christian


