What Is The Need for Chromatographic Techniques In Drug Development
Table of Contents
- Introduction and Background
- Chromatographic techniques and traditional techniques
- Why chromatographic techniques are required for analysis?
- Traditional techniques vs chromatographic techniques
- Advantages of chromatographic techniques
- Applications of chromatographic techniques
- Conclusion
Introduction and Background
Chromatographic techniques are the backbone of pharmaceuticals development. Pharmaceuticals development is impossible without the use of chromatographic techniques. However, most of the chemists don’t know why chromatographic techniques are widely used in pharma industries. That is why I decided to share my skill-based knowledge on ” Need for Chromatographic techniques”. Having read this article all your doubts will be cleared and you will be able to answer questions like:
- What is chromatographic techniques?
- What are the different types of chromatographic techniques?
- Why chromatographic techniques are widely used in the Pharmaceutical industry?
- Which chromatographic techniques are widely used in pharma industries?
- What are the differences between chromatographic techniques and traditional techniques?
- Why pharmaceuticals development is not possible using traditional techniques?
- What are the advantages of chromatographic techniques?
Chromatographic techniques and traditional techniques
Traditional techniques
The following techniques are used as traditional techniques
- Chemical method of analysis and
- Spectroscopic method of analysis
The above methods are not specific and selective; it means the result obtained by the above method may or may not be correct. That is why pharmaceutical development is impossible using these traditional techniques.
Chemical method
Generally following volumetric titrations are widely used for the pharmaceuticals analysis:
- Acid base titration
- Oxidation -reduction titration
- Iodometric titration
- Iodimetric titration
- Sodium nitrite titration
- Complexometric titration
- Non aqueous titration or perchloric titration
Note: Gravimetric methods are not correct that is why this technique is rarely used in the pharmaceutical analysis
Spectroscopic methods
Generally following spectroscopic methods are widely used for the pharmaceuticals analysis:
- Ultraviolet spectroscopy (UV) and
- Infrared spectroscopy (IR)
Chromatographic techniques
The term chromatography was given by Tswett in 1906, he also published some papers on liquid chromatography. In 1941, Martin and Synge tried to separate amino acids in wool samples using a column packed with silica gel and a mixture of Butanol and chloroform as a mobile phase. He also explained the theoretical aspect of procedure and got Nobel Prize in 1952. Since that time LC technique has become a versatile technique available for chemists because of its simplicity and capacity for high resolution.
Types of chromatographic techniques:
- Complete chromatography
- Continuous chromatography
Complete chromatography
Following techniques come under the complete chromatography:
- Thin layer chromatography or TLC and
- Paper chromatography or PC
Thin layer chromatography or TLC
It is widely used in industries for qualitative analysis during drug development e.g. identification tests, related substances tests, purity tests, monitoring the reaction (during drug development) etc. This technique is specific and selective and accepted by all regulatory agencies.
Acceptance criteria of TLC
The Rf value of the principal spot obtained from the test solution correspond to that obtained from the standard solution
Paper chromatography or PC
It is used in industries for qualitative analysis e.g. identification tests, related substances tests, purity tests etc. This technique is specific and selective and accepted by all regulatory agencies. This technique is specific and selective and accepted by all regulatory agencies.
Acceptance criteria of PC
The Rf value of the principal spot obtained from the test solution correspond to that obtained from the standard solution
Continuous chromatography
Following techniques are widely used in the continuous chromatography
- High – pressure liquid chromatography or HPLC
- Gas chromatography or GC
Both HPLC and GC are specific and selective methods and are widely used in the industries for both qualitative and quantitative analysis.
Why chromatographic techniques are required for analysis?
Case study-1
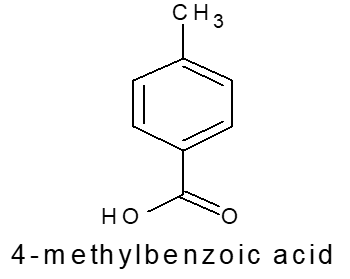

Let us consider a sample containing 4 – methyl benzoic acid and 2 – methyl benzoic acid in the ratio of 50:50. How content each will be calculated?
Using chemical method
Since both 4 – 4-methyl benzoic acid and 2 – methyl benzoic acid are acids hence can be estimated by using acid-base titration. Since both molecules 4 – methyl benzoic acid and 2 – methyl benzoic acid contain -COOH group and hence both molecules will be titrated simultaneously. Hence the correct result will not be obtained and consequently traditional /chemical titration method is not suitable for such molecule
Using chromatographic/HPLC method
Since the chromatographic method is selective and specific and hence one can get two peaks (about 50% each) in the chromatogram. That is why the chromatographic method is correct for such molecules
Case study-2
Let us consider a sample contains phenol and Benzoic acid in ration of 10 :90. How content each will be calculated using traditional method and chromatographic method?
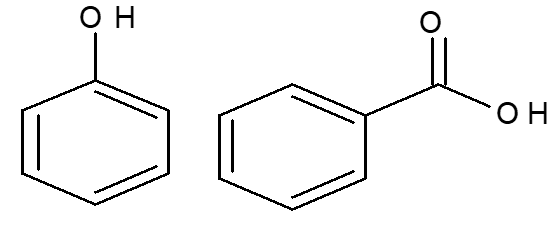
Using chemical method
Phenol contains the -OH group and Benzoic acid contains -COOH group and hence can be estimated by acid-base titration. But acid base titration will not give the correct result because each -OH group and -COOH group will be titrated simultaneously. Hence it will be difficult to distinguish between each and consequently correct results will not be obtained. Therefore, the traditional /chemical titration method is not suitable for such molecules
Using chromatographic/HPLC method
Since chromatographic method is selective and specific in nature and hence one can get two peaks (about 10% Phenol and 90% for Benzoic acid) in the chromatogram. That is why chromatographic method is correct for such molecules
Traditional techniques vs chromatographic techniques
| S.N | Chromatographic techniques | Traditional techniques |
| 1 | Specific and selective | Not specific and selective |
| 2 | Can be used for both qualitative and quantitative analysis | Mainly used for qualitative analysis |
| 3 | Accepted by all regulatory agencies | Not accepted by all regulatory agencies |
| 4 | Related substance can be performed | Related substances test can not be performed |
| 5 | Highly sensitive with low detection limit | Low sensitive |
Advantages of chromatographic techniques
- Specific and selective. It means there is not any interference/merging of peaks
- Helpful in controlling the quality of drug at different stages
- Accepted by all regulatory agencies
- Method can be easily validated
Applications of chromatographic techniques
- Identification test
- Assay
- Related substances
- Chiral purity
- Content test
Conclusion
The chromatographic technique is the backbone of pharmaceutical analysis. That is why it is widely used in the industries. Now I hope all your doubts related to the use of chromatographic technique and traditional techniques have been cleared. For any doubts or questions related to this post write in the comment section and I will answer the same on a priority basis.
You may also want to check out other articles on my blog, such as:
- Difference between HPLC and GC
- How to develop a method using GC-MS?
- Need of Chromatographic Method in Drug Development
- What is the Chiral Gas Chromatography?
- How to decide system suitability test (SST)?
- Allowable GC Method Adjustment
- How to develop the HPLC method for basic compounds?
- How to develop the HPLC method for acidic compounds?
- How to develop the HPLC method for non-polar compounds?
- What should be the Analytical method development approach?
- GLP, GDP and OOS-OOT.
FAQs
What is the importance of chromatographic techniques?
Chromatographic techniques are widely used in drug development due to their selectivity and specificity,
What are the 5 uses of chromatography?
Chromatography techniques are widely used for
- Identification test
- Purity test
- Related substances test
- Assay test and
- Content test
References:
- IP
- USP
Abbreviations’
- TLC: Thin layer chromatography
- PC: Paper chromatography
- GC: Gas chromatography
- HPLC: High pressure liquid chromatography


