How to Decide Chromatographic Resolution
Table of Contents
- Introduction and outcome
- Resolution
- How Resolution is calculated?
- Factors affecting Resolution
- Conclusion
Introduction and outcome
Resolution-controlling factors in HPLC; Play an important role during chromatographic separation. Resolution is an integral part of the system suitability (SST) test. This article will clear all your doubts related to Resolution and the factors that affect resolution. Having read this article you will be able to answer questions like:
- What is resolution and how it is calculated?
- What are the factors affecting the Resolution?
- What is the role of Resolution in HPLC method development?
- What are the acceptance criteria for Resolution?
Resolution
Resolution is the numerical measurement between two adjacent peaks in the chromatogram. It tells about the separation between the adjacent peaks. It is denoted by R.
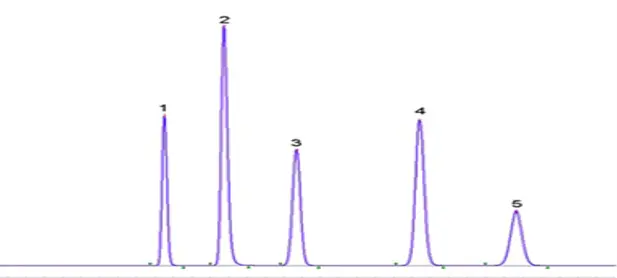
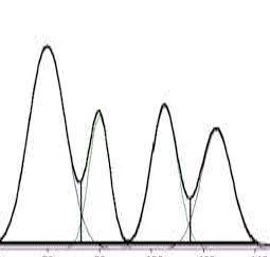
In the above Chromatograms, figure-1 all peaks are well separated whereas in Figure-2 adjacent peaks are merging. Chromatogram-2 is not acceptable and hence resolution-controlling factors must be adjusted to get the separation between the adducent peaks.
How Resolution is calculated?
Several formulas are available to calculate the resolution out of which the following formulas are widely used in pharmaceutical analysis:
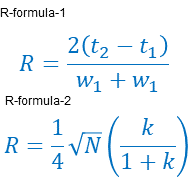
Where: R is Resolution, w is peak width, Nis column efficiency, k is capacity factor, and 2 are peak-1 and peak -2
R-formula-1 is used to calculate the resolution during routine analysis whereas R-formula-2 is used to modify chromatographic conditions to increase the separation during method development.
Case studies
- Generally, good resolution is easily achieved between the non polar molecules e.g. Naphthalene, Anthracene. In such cases R more than 2 is easily achieved.
- In some typical compound R less than 1 is also kept. In Erythromycin USP, Resolution between Related compound n and Erythromycin is not less than 0.8
Factors affecting Resolution
Following are the resolution controlling factors in HPLC:
- Column chemistry and stationary phase purity: R depends upon column chemistry and purity of the stationary phase. Colun with pure stationary phase give high resolution between the peaks
- Column length: R is directly proportional to the column length
- Particle size: R is inversely proportional to the particle size. On decreasing particle size R increases.
- Structure of the molecule: R also depends upon the structure of the molecule. Generally, isomeric molecules have low resolution compared to non-isomeric molecules
- Peak shape: R is directly proportional to the peak sharpness
- Column efficiency or theoretical plate: R is directly proportional to the column efficiency
- Tailing factor: R is inversely proportional to the tailing factor
- pH: R of some of the molecules are pH dependent. Basic molecules have high R at high pH whereas acidic molecules having high R are at low pH
- Column temperature: R is the function of column temperature, It may increase or decrease depending on the molecule characteristics
- Buffer: R is directly proportional to the buffer concentration
- Injection volume: R is inversely proportional to the buffer concentration
- Sample concentration: R is inversely proportional to the sample concentration
- Retention time: R is directly proportional to the retention time
Acceptance criteria for Resolution
- R should be more than 1.5 or R≥1.5 with baseline separation
- In some case R< 1.5 should also be acceptable with proper scientific justification
- R must be kept based on trend data
Importance/applications of Resolution in HPLC method development
- It tells about the capacity of the method
- The higher the R better the method
- It is used in SST (system suitability test)
Conclusion
Hope this post, clears all your doubts related to the Resolution or factors affecting the resolution. Now you can use control the different factors affecting the resolution during method development. Write your questions/suggestions related to this article in the comment section.
References:
- Erythromycin USP monograph
- Improving Resolution, waters.com
Abbreviations:
- R: Resolution
- SST: System suitability test
- HPLC: High performance liquid chromatograms



Very helpful and informative
Useful Post..